| Introduction

Thumbtack 던졌을 때, Head가 나올 확률은? ... 5:5 일까?
일단 몇 번 던져봅니다!
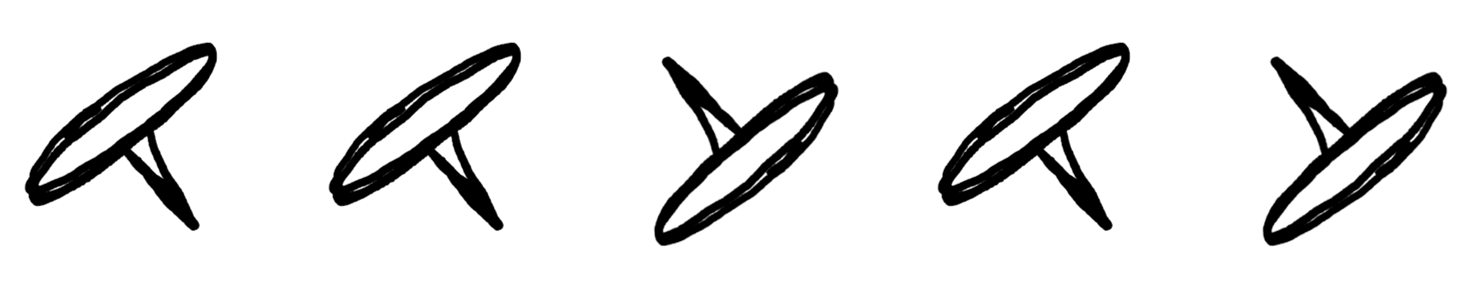
그러면 ... Head: $ \frac{3}{5} $ ... Tail: $ \frac{2}{5} $
| Binomial Distribution
Discrete probability distribution
"n" independent yes/no experiments (Bernoulli experiment)
Filps are i.i.d. (Independent Identically Distributed)
$$ P(H)=\theta $$
$$ P(T)=1-\theta $$
$$ P(H, H, T, H, T)= \theta^3 \cdot (1-\theta)^2 $$
Let's say
$$ D \ (\mbox{Data}) : H, H, T, H, T $$
$$ n = 5 $$
$$ k = a_H = 3 $$
$$ P = \theta $$
"$ \theta $ 가 Given 일 때 D 라는 Data 가 관측될 확률"
$$ P(D\mid \theta)=\theta^{\ a_H} \cdot (1-\theta)^{\ a_T} $$
그렇다면 이 정보를 이용해서 어떻게 $ \frac{3}{5}, \frac{2}{5} $ 의 값에 도달할 수 있을까요?
우리의 가정 Our hypothesis
: The gambling result of tumbtack follows the binomial distribution of $ \theta $
어떻게 해야 이 가정이 강해질까요? Hypothesis 가 참이라고 말할 수 있을까요?
→ Finding out "the best candidate of $ \theta $ "
| Maximum Likelihood Estimation of $ \theta $
"관측된 Data 의 확률을 최대화하는 $ \theta $ 를 찾아내는 것"
$ P(D \mid \theta) $ 를 최대화하는 argument $\theta$ 를 찾아내고, 이를 $\hat{\theta}$ 라 하겠다.
$$ \hat{\theta}=argmax_{\theta} \ P(D \mid \theta) $$
그렇다면 전개해보자.
$$
\begin{align*}
\hat{\theta} &= argmax_{\theta} \ P(D \mid \theta) \\
& = argmax_{\theta} \ \theta^{\ a_H} \cdot (1-\theta)^{\ a_T}
\end{align*}
$$
... square ... 풀기 어렵다... Log 적용 (monotonic increase function)
$$
\begin{align*}
\hat{\theta} &= argmax_{\theta} \ ln P(D \mid \theta) \\
& = argmax_{\theta} \ ln \left\{ \theta^{\ a_H} \cdot (1-\theta)^{\ a_T} \right\} \\
& = argmax_{\theta} \ \left\{a_H\ ln \theta + a_T\ ln (1-\theta) \right\}
\end{align*}
$$
... Maximum ... 미분 ...
$$ \frac{1}{\theta} \cdot a_H + \frac{1}{1-\theta} \cdot a_T=0 $$
$$ \therefore \theta = \frac{a_H}{a_H+a_T} = \frac{3}{5} $$
When $ \theta $ is $ \frac{a_H}{a_H+a_T} $ , the $ \theta $ becomes the best candidate from the MLE perspective.
$$ \hat{\theta} = \frac{a_H}{a_H+a_T} $$
"MLE 관점에서 최적화하여 추론된 $ \hat{\theta} $ 을 구할 수 있다."
간단하게 던져봐서 알아냈던 $ \frac{3}{5} $ 라는 확률이 ...
사실은 binomial distribution, MLE, 최적화 등등을 거쳐서 나온 것 !
| Error bound
회장님: 자 그러면 ... 내가 시간이 남아서 50번을 더 던져봤더니 H가 30번, T가 20번 나왔어.
공학도: Your additional trials are valuable to ... "추론한 것에 대한 Error 가 줄어든다."
$$ P(\ |\ \hat{\theta}-\theta^* | \geqslant \varepsilon\ ) \leqslant 2e^{-2N\varepsilon^2} $$
추론한 $ \hat{\theta} $ 와 True $ \theta^* $
"이 둘의 차이가 특정 Error bound 보다 클 확률"
1. Error 가 크면 ... 우항이 작고 ... Error 가 발생할 확률은 작아진다.
2. N 이 크면 ... 우항이 작고 ... Error 가 발생할 확률은 작아진다.
(추론한 $ \hat{\theta} $ 와 실제 $ \theta^* $ 의 Error 발생 확률이 낮다.)
To obtain $ \varepsilon=0.1 $ with 0.01% case,
몇 번 던져야 하나요? 즉 ... N = ? … 대략 500번 (계산 가능)
| Probably Approximate Correct (PAC) Learning
This is Probably Approximate Correct (PAC) learning …
Probably (0.01%) Approximate ($\varepsilon=0.1$)
확률 범위 0.01% 에서 "오차범위 $ \varepsilon=0.1 $내 Correct 한 $\theta$ 를 찾은 것"
SUMMARY
Thumbtack 던졌을 때 Head가 나올 확률은 몇일까?
그 확률을 추론하기 위하여 MLE 관점 적용!
MLE를 통해 "관측된 Data의 확률을 최대화하는 Parameter $ \theta $ " 를 추론할 수 있다.
(Binomial distribution 가정)
Error bound 또한 계산 가능하기 때문에, Probably Approximate Correct (PAC) Learning 가능!
... Probably 0.01% ... Approximate 0.1 error
"$ \theta $ 가 Given 일 때 D 라는 Data가 관측될 확률" 을 특정 Binomial 분포로 가정
$$ P(D\mid \theta)=\theta^{\ a_H} \cdot (1-\theta)^{\ a_T} $$
MLE: "Data가 관측될 확률 $ P(D \mid \theta) $" 를 최대화하는 $ \theta $ 를 찾고, 이를 $\hat{\theta}$ 라 하겠다.
$$ \hat{\theta}=argmax_{\theta} \ P(D \mid \theta) $$
이를 통해, 우리가 궁금했던 "$ \theta $ 로 정의된 확률" 을 추론하였다.
추론 결과: 앞 면이 나온 횟수 / 전체 던진 횟수
$$ \hat{\theta} = \frac{a_H}{a_H+a_T} $$
Reference
문일철 교수님 강의
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=3AwO0O6hWBI&list=PLbhbGI_ppZISMV4tAWHlytBqNq1-lb8bz&index=3
'Study > Lecture - Basic' 카테고리의 다른 글
| W2.L4. Entropy & Info. Gain (0) | 2023.04.28 |
|---|---|
| W2.L1-3. Rule-Based ML (0) | 2023.04.28 |
| W1.L4. Probability & Distribution (0) | 2023.04.28 |
| W1.L3. MAP (0) | 2023.04.28 |
| W1.L1. Motivation (0) | 2023.04.27 |



